Follistatin-344: A Multifaceted Peptide in Scientific Exploration
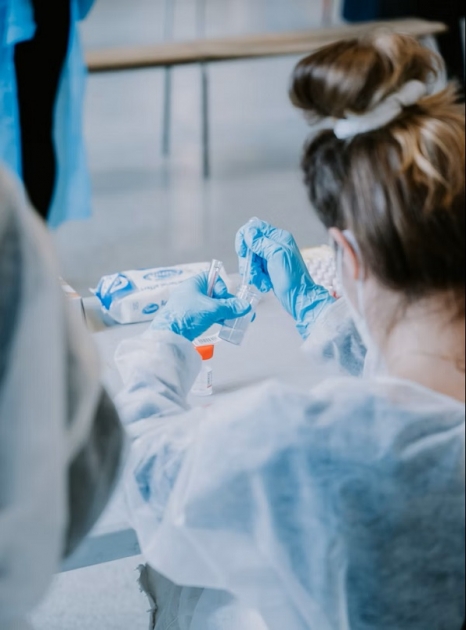
Peptides have long been investigated for their diverse biochemical properties and potential implications in scientific research. Among them, Follistatin-344 has emerged as a molecule of interest due to its interactions with members of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) superfamily.
It has been hypothesized that this peptide might play a role in cellular regulation, tissue remodeling, and molecular signaling. Given its unique structural characteristics, researchers are exploring its implications in fields such as regenerative science, biomaterials, and molecular biology.
Structural and Functional Properties of Follistatin-344
Follistatin-344 is a synthetic analog of endogenously occurring follistatin, a glycoprotein known for its interactions with activin and myostatin. Investigations purport that this peptide might act as an antagonist to myostatin, a molecule theorized to regulate skeletal muscle development. By modulating these interactions, Follistatin-344 seems to contribute to various physiological processes within a research model.
Interactions with Myostatin and Activin
Research indicates that Follistatin-344 might exhibit binding properties that interfere with myostatin activity. Myostatin is theorized to play a role in limiting muscle cell growth, and its mitigation may lead to alterations in cellular proliferation and differentiation. Additionally, activin, another member of the TGF-β family, has been investigated for its possible involvement in cellular signaling pathways. It has been hypothesized that Follistatin-344 might regulate activin interactions, potentially supporting tissue development and molecular communication.
Potential Role in Tissue Research
Investigations purport that Follistatin-344 might contribute to extracellular matrix remodeling. The extracellular matrix is a complex network of proteins that provides structural support to tissues and organs. Research indicates that peptides interacting with matrix components may support cellular adhesion, migration, and regeneration. These properties suggest that Follistatin-344 may be explored for implications in biomaterials and tissue engineering.
Peptide-Based Signal Modulation Research
It has been hypothesized that Follistatin-344 might serve as a signaling molecule that interacts with growth factors and cytokines. These interactions appear to support cellular responses, including proliferation, differentiation, and molecular regulation. Research suggests that peptides with signaling properties may be explored for their potential implications in regenerative science and molecular biology.
Possible Implications in Scientific Research
The versatility of Follistatin-344 has led to its exploration in various scientific domains. Researchers are investigating its potential implications in biomaterials, regenerative science, and molecular signaling.
Biomaterials and Tissue Investigations
It has been hypothesized that Follistatin-344 might contribute to the development of biomaterials with better-supported biocompatibility. Peptide-functionalized scaffolds are being explored for their potential to support cellular adhesion and tissue regeneration. Investigations suggest that incorporating peptides into biomaterials may support their structural and functional properties, making them suitable for implications in reconstructive research.
Regenerative Science
Research suggests that Follistatin-344 may be explored for its potential role in regenerative science. Peptides that interact with growth factors and extracellular matrix components may be explored for their potential to support tissue repair mechanisms. Scientists are examining peptide-based formulations that may contribute to cellular proliferation and matrix remodeling, offering promising avenues for regenerative implications.
Molecular Biology and Signal Transduction Research
Follistatin-344 has been theorized to play a role in molecular signaling pathways. Investigations purport that peptides with signaling properties might be explored for implications in cellular communication and biochemical regulation. Research suggests that Follistatin-344 may be explored for its interactions with molecular regulators, potentially leading to advancements in signal transduction studies.
Peptide-Based Biosensors
Peptides may be investigated for their potential implications in biosensor technology. It has been hypothesized that peptide-functionalized biosensors might exhibit selective interactions with biological markers, supporting precise detection of molecular changes. These biosensors may be explored for implications in diagnostic research and environmental monitoring.
Peptides in Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is an emerging field that integrates molecular components into structures on the nanoscale. Research indicates that peptides might be incorporated into nanomaterials to support their functional properties. Peptide-based nanoparticles may be explored for implications in imaging technologies and biomedical engineering.
Peptides in Environmental Science
Peptides may be investigated for their potential implications in environmental science. It has been theorized that peptide-based materials might contribute to biodegradable coatings, pollutant detection, and microbial regulation. These implications suggest that peptides may be explored for sustainable solutions in environmental research.
Future Directions and Considerations
While research into Follistatin-344 continues to expand, further investigations are necessary to elucidate its mechanisms and optimize its implications. It has been theorized that peptide modifications, such as structural alterations and conjugation with biomolecules, might support their stability and functionality. Scientists are exploring innovative exposure systems that may improve peptide integration into biomaterials and research formulations.
Conclusion
Follistatin-344 represents a fascinating area of scientific exploration, with potential implications spanning biomaterials, regenerative science, and molecular biology. Research suggests that this peptide may play a role in cellular communication, tissue remodeling, and molecular regulation within an organism. As investigations continue, the versatility of Follistatin-344 may pave the way for novel advancements in scientific research and technological innovation. For more useful peptide data, visit this FST-344 study.
References
[i] Winbanks, C. E., Rigby, P. W. J., & Underwood, C. J. (2018).
Myostatin and activin blockade by engineered follistatin results in hypertrophy and improves dystrophic pathology in mdx mouse more than myostatin blockade alone. Skeletal Muscle, 8, Article 19.
[ii] Hayashido, Y., & Shimatsu, Y. (2019).
Discovery of a follistatin-derived myostatin inhibitory peptide. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 513(2), 435–441.
[iii] Tsuchida, K., & Sakurai, H. (2009).
Myostatin inhibition by a follistatin‑derived peptide ameliorates the pathophysiology of the muscular dystrophy model mice. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284(9), 5305–5313.
[iv] Rodino-Klapac, L. R., Haidet, A. M., Kota, J., Handy, C., Kaspar, B. K., & Mendell, J. R. (2016).
Follistatin gene therapy improves ambulation in Becker muscular dystrophy. Molecular Therapy, 24(3), 515–524.
[v] Schafer, M. J., & LeBrasseur, N. K. (2013).
Effects of the activin A–myostatin–follistatin system on aging bone and muscle progenitor cells. Journal of Gerontology: Biological Sciences, 68(4), 454–464.